Common Issues with Reflective Yarn

MAX Reflective Accessories Design Director
Reflective yarn is a crucial component in a wide range of safety and fashion applications, from high-visibility workwear to stylish accessories. Its ability to reflect light back to its source makes it invaluable for enhancing visibility in low-light conditions, contributing significantly to safety.
However, working with reflective yarn can present some challenges. At MAX, a leading professional reflective accessory supplier in China, we understand these challenges and are committed to providing solutions. This blog post will address some common issues encountered when using reflective yarn and offer practical solutions based on our extensive experience.

Reflective yarn breakage
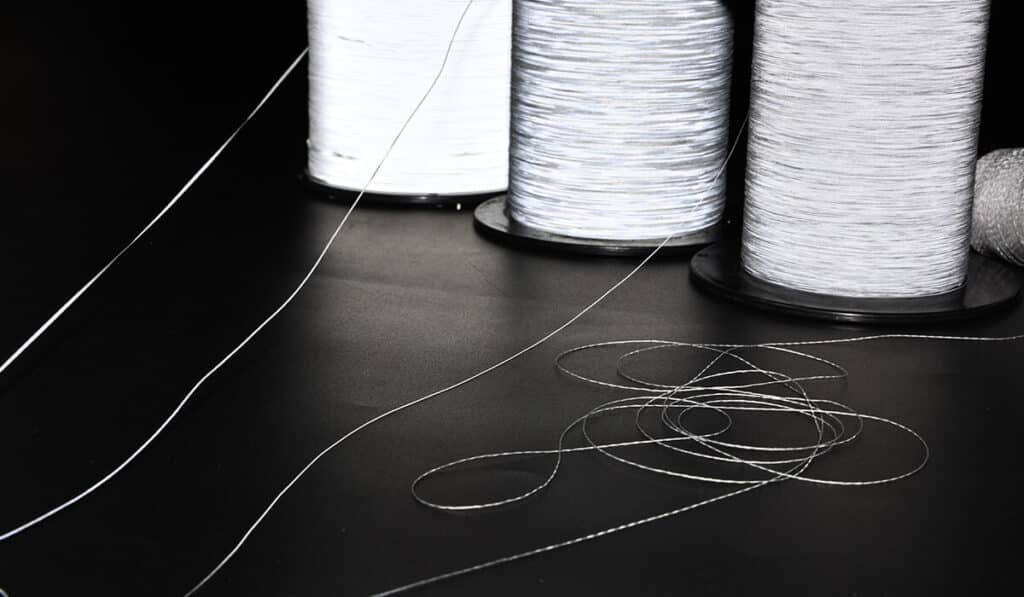
One of the most frequent problems encountered when using reflective yarn is thread breakage. Due to its delicate nature – some variants can be as thin as 0.25mm or even 0.35mm – reflective yarn is susceptible to breaking under tension. This can be particularly problematic during high-speed applications like industrial weaving or embroidery. The primary culprit is often improper tension control or inconsistent force transmission during the application process.
Solutions:
- Precision tuning: Calibrate machinery to ensure tension settings match the yarn’s thickness. Start with low tension and gradually increase while monitoring performance.
- Equipment maintenance: Regularly inspect and polish machine parts (e.g., needles, guides) to eliminate sharp edges or burrs that could damage the yarn.
- Speed control: Reduce operational speed during initial setup or when using finer yarns. Gradually increase speed once stability is confirmed.
- Pre-production testing: Run multiple tests to identify optimal tension, speed, and thread path configurations before full-scale production.
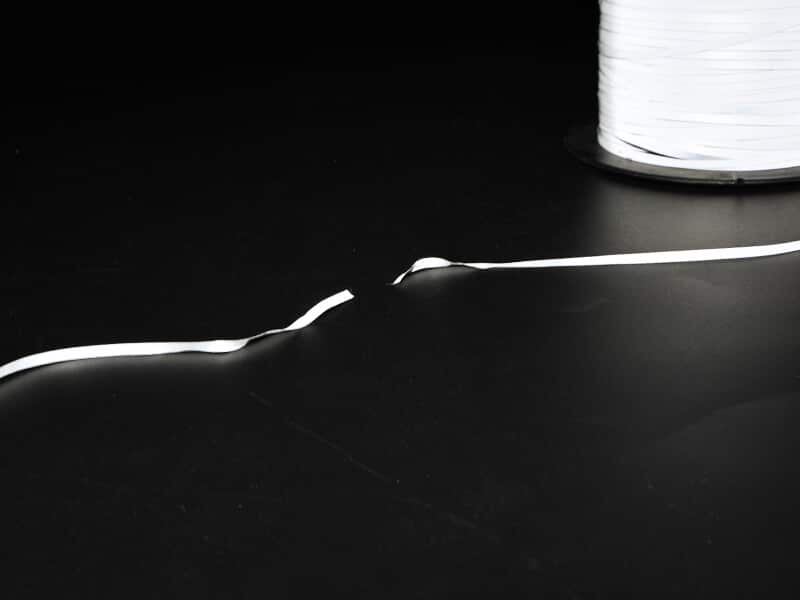
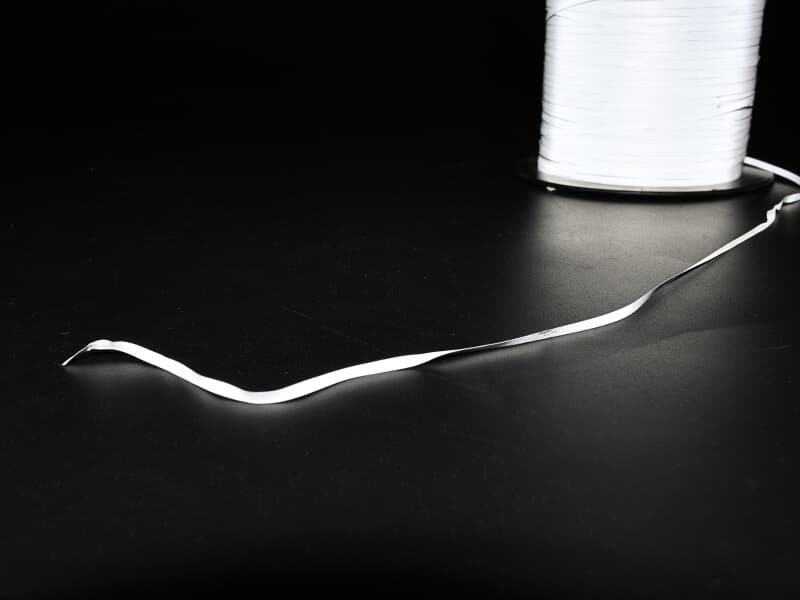


Reflective yarn twisting
Reflective yarn’s lightweight and narrow profile make it susceptible to twisting during weaving or knitting. While twisting doesn’t compromise functionality, it can affect aesthetics or alignment in applications requiring precise reflective patterns.
Solutions:
- Double-sided reflective yarn: Use yarn with reflective coatings on both sides. Even if twisting occurs, one reflective surface will always face outward.
- Thicker/wider yarn options: For heavy-duty applications, opt for thicker (e.g., 0.5mm) or wider yarn, which resists twisting due to its increased rigidity.
- Hybrid weaving: Combine reflective yarn with a stabilizing core thread (e.g., polyester or nylon) to minimize movement and maintain alignment.
- Tension adjustment: Ensure even tension across all yarns in the loom or knitting machine to reduce uneven stress that causes twisting.
The difference between reflective thread and yarn
Uneven reflective performance
Inconsistent reflectivity can occur due to uneven coating application, contamination during production, or wear and tear. For example, dirt, oil, or abrasion might block the reflective microprisms on the yarn’s surface, reducing its light-return capability.
Solutions
- Quality control at source: Partner with suppliers (like MAX) that adhere to strict manufacturing standards, ensuring uniform coating thickness and purity.
- Post-processing care: Avoid exposing reflective yarn to harsh chemicals, oils, or abrasive surfaces during production. Clean machinery regularly to prevent contamination.
- Protective coatings: Apply a clear protective layer (e.g., UV-resistant laminate) to shield the reflective surface from environmental damage.
- Regular inspections: Test finished products for reflectivity using standardized tools (e.g., retroreflectometers) to catch issues early.
Compatibility with fabrics
Reflective yarn may not bond well with certain fabrics, leading to peeling, fraying, or reduced durability. For instance, slippery synthetic fabrics (e.g., nylon) or heavily textured materials can challenge adhesion during sewing or heat-pressing.
Solutions
- Adhesive backing: Use reflective yarn with a heat-activated adhesive layer for seamless integration into fabrics during thermal bonding.
- Reinforced stitching: For sewing applications, pair reflective yarn with a strong base thread (e.g., bonded nylon) and use a zigzag stitch to enhance grip.
- Fabric pretreatment: Clean and prime fabric surfaces with a mild adhesive spray or silicone-based solution to improve yarn adhesion.
- Customized combinations: Work with suppliers to develop hybrid yarns tailored to specific fabric types (e.g., moisture-wicking blends for sportswear).
Choosing the right reflective yarn supplier
The quality of reflective yarn and the technical support provided by your supplier play a pivotal role in overcoming these challenges. At MAX, we offer:
- Diverse product range: From ultra-thin (0.25mm) to heavy-duty (1.0mm) yarns, including double-sided and adhesive-backed options.
- Technical expertise: Our team provides guidance on yarn selection, machinery setup, and troubleshooting.
- Custom solutions: Tailored yarn blends, coatings, or widths to meet unique application requirements.
Conclusion: Common issues with reflective yarn
While working with reflective yarn can present some challenges like breakage and twisting, these issues can be effectively addressed with the right knowledge and approach. By understanding the causes and implementing the solutions outlined in this blog, you can ensure optimal performance and achieve the desired reflective effect in your products.
At MAX, we’re committed to helping you navigate these challenges with high-quality materials and expert support. Contact us today to explore how our reflective yarn solutions can elevate your projects!

Related blogs

Related products

Reflective Heat Transfer Vinyl